Nanotechnology is one of the new branches of the industry with a focus on the particle size and shape at nano scale (1nm-100nm). Nanotechnology can be divided into several categories which is (0-D) nanoparticles such as quantum dots and nanodots, (1-D) nanowires and nanorods, (2-D) carbon nanotubes (CNT) and multi-layered biopolymers and the last are (3-D) which refer to bulk nanostructures like nanopowder. Nanotechnology has many advantages in various fields such as in the energy industry, medicine, solar cells, robotics and technology, mechanical, electrical and semiconductor industries. The advantages of nanotechnology are that it has high surface area to volume ratio and can be used in development of new device and current technology.
One of the nanotechnology branches is semiconductor nanocrystals. Semiconductor are insulating materials and conductors at the same time. This material is suitable for electronic application such as diodes, transistor, and integrated circuits. Zinc oxide is one of the semiconductor materials that have many advantages such as wide band gap and large exciton binding energy 60meV. This enables it to be used in many modern devices such as sensors, biomedicine, and optoelectronics.
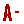
Zinc oxide nanostructure has been synthesis using hydrothermal method produce (1-D) structure. By controlling the nanostructure of this material, the application of semiconductor materials can be improved. The crystalline forms of nanostructures produced using hydrothermal methods are nanoflower and nanorods based on Figure 1. This semiconductor nanostructure shows properties of larger band gap as the surface area increases with the same volume. These variations give rise to the properties and advantages possessed by the nanomaterials.





The different morphology of zinc oxide nanostructures growth using the hydrothermal method with different pH (A)pH 7, (B) pH 8, (C) pH 9, (D) pH 10 and (E)pH 11.
By,
Nurul Hidayah binti Ramli
Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM)
"2nd runner up for the Science Article Writing Competition"
Date of Input: 16/11/2020 | Updated: 16/11/2020 | nursyahirah
MEDIA SHARING