Carbon dioxide (CO2) reduction through photocatalysis is considered a promising way to mitigate the abundance of this greenhouse gas in the earth's atmosphere. In this work, blue-fluorescent carbon quantum dots (CQD) were synthesized via a facile top-down hydrothermal method utilizing empty fruit bunch (EFB) biochar of oil palms as the precursor. The as-synthesized CQD with varying loading content (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 wt.%) were incorporated together with commercial copper (I) oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles using a simple wet impregnation method to form (CQD/Cu2O) nanocomposites. The CQD, Cu2O and the prepared CQD/Cu2O nanocomposites were then applied for gas-phase photocatalytic CO2 reduction. The experiments were performed under visible light irradiation in a self-designated photoreactor which was connected to an online Gas Chromatography (GC). It was demonstrated that the CQD/Cu2O photocatalyst with 2 wt. % of CQD was able to give the highest photoactivity among all other photocatalysts with an improvement of 54% in photoactivity than that of pure Cu2O.
The physicochemical properties of the best-performed photocatalyst were studied to find the correlation of these properties with the marked photoactivity of this particular photocatalyst. The presence of CQD in the composite was confirmed by High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) micrographs where CQD with diameter 2.2-5.7 nm were decorated uniformly onto the surface of Cu2O nanoparticles. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) further revealed the deposition of CQD on the surface of Cu2O. The considerable improvement in the photoactivity of this photocatalyst was due to the improved charge separation efficiency at the CQD-Cu2O interphase at the optimum loading, where CQD serve as electron acceptor to reduce the charge recombination rate of Cu2O. This behavior was supported by highest PL quenching of this nanocomposite than that of pure Cu2O. Besides Tauc's relation from absorbance data further revealed the band gap reduction of this nanocomposite. Apart from that, band alignment of CQD/ Cu2O, charge carriers transfer and separation as well as possible reaction pathways for CO2 photoreduction was proposed based on the research findings. The photocatalyst also exhibited excellent stability under repeated cycles of photoreaction. Overall, the considerable enhancement in the photoactivity of the nanocomposite describes the importance of the CQD to facilitate the high electron demanding CO2 photoreduction reaction to ethane.
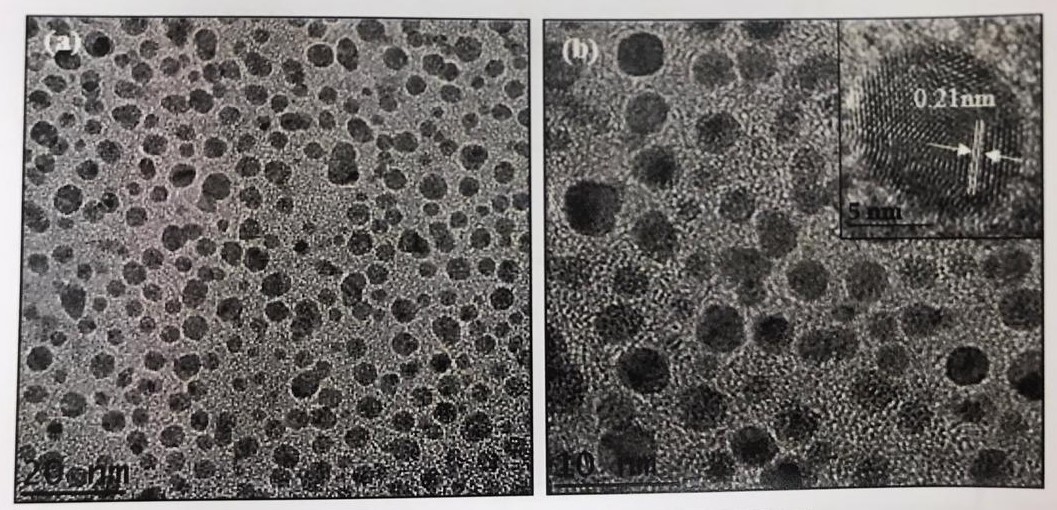
HRTEM Image of CQD
*Abstract of the thesis (Master of Science) by Tharani Kulandaivalu.
For further information please contact:
Associate Professor Dr Suraya Abdul Rashid
Chairman
suraya_ar@upm.edu.my
Date of Input: 25/02/2022 | Updated: 07/10/2022 | roslina_ar
MEDIA SHARING